- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
A pricing model is more than just setting a price tag; it’s a strategic decision that can make or break your business. Whether you are launching a product, entering a new market, or trying to optimize revenue, understanding pricing models is crucial.
Choosing the right pricing model impacts how customers perceive your brand, market competitiveness, and ultimately, bottom line. This article explores the nuances of pricing models, types, challenges, and strategies to help you make informed decisions for your business.

A pricing model is a systematic approach businesses use to set prices for their products or services. It considers various factors such as:
The primary goal of any pricing model is to maximize profitability while ensuring value for customers. A successful pricing model balances cost, value, and competition to achieve long-term business sustainability.
This traditional model calculates the total cost of producing a product and adds a markup percentage to ensure profit.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A retailer purchasing shoes at $50 per pair may apply a 50% markup, setting the retail price at $75.
This model sets prices based on the perceived value of a product to the customer.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Apple’s iPhones are priced significantly higher than competitors due to their perceived quality and innovation.
Businesses align their pricing with competitors to stay relevant in the market.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Gas stations often use competitive pricing by monitoring nearby prices and setting theirs accordingly.
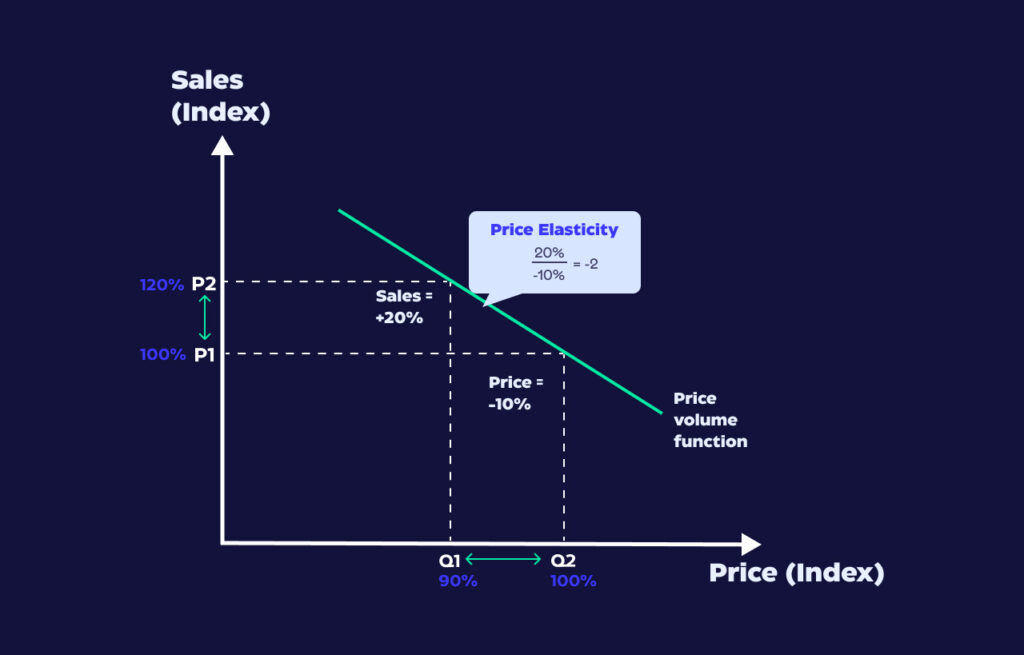
Prices are adjusted in real-time based on demand, inventory, or market trends.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Airlines adjust ticket prices based on demand, seasonality, and time of purchase.
Customers pay a recurring fee for access to products or services.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Netflix offers tiered subscription plans for access to streaming services.
A combination of free and premium offerings, this model provides basic services for free while charging for advanced features.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Spotify offers free access with ads and premium access with additional features like offline listening.
This unconventional model lets customers decide the price they’re willing to pay.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Some restaurants and donation-based software platforms use this model.
Selecting the correct pricing model is a strategic decision that affects several aspects of a business:
A pricing model is the backbone of any business’s revenue strategy. By understanding the types, benefits, and challenges of pricing models, businesses can craft strategies that resonate with their target audience and market conditions.
Success in pricing requires regular review, customer feedback, and adaptability. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, investing in a sound pricing model is an investment in your long-term growth and profitability.
Make the most of these insights to define a pricing strategy that aligns with your goals, and watch your business thrive in competitive markets.
Yes, many companies use hybrid approaches, such as combining subscription models with freemium strategies.
Monitor metrics like profit margins, customer acquisition cost, and retention rates.
Some models are more common in certain industries (e.g., subscription models in SaaS), but they can often be adapted to suit different needs.





We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!