- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
Revenue forecasting is only as reliable as the data that feeds it. Understanding how data accuracy impacts revenue forecasting is essential for pricing leaders, finance teams, and revenue operations professionals who rely on projections to guide inventory, budget, and growth strategy.
Even minor inaccuracies in pricing, demand signals, or competitive data compound quickly across reporting periods. The result is forecast variance, margin instability, and executive distrust in analytics systems.
Below is a detailed examination of how data quality directly influences forecast performance and long term revenue outcomes.
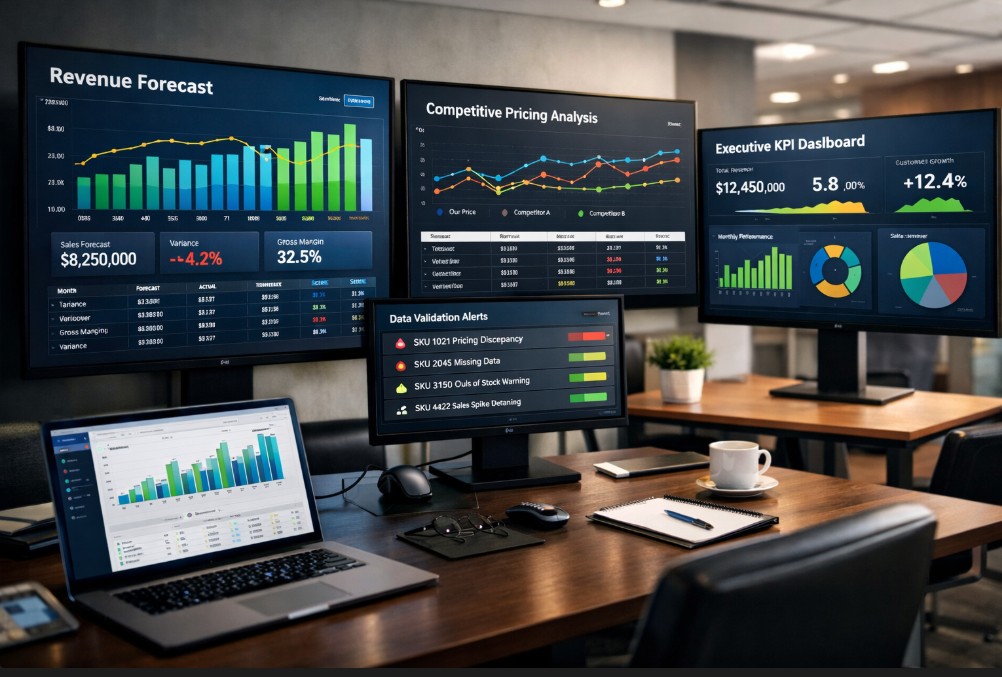

Data accuracy in revenue forecasting refers to the reliability, completeness, timeliness, and consistency of inputs such as pricing, demand, and competitive signals. Accurate data reduces forecast variance and margin distortion. Inaccurate or delayed inputs cause compounding errors that destabilize revenue projections and strategic planning.
Data accuracy is often misunderstood as a technical IT concern. In reality, it is a strategic revenue driver.
Forecast models rely on:
Historical sales volume
Current pricing
Promotional adjustments
Competitive pricing signals
Inventory levels
Seasonality factors
If even one of these inputs is outdated or inconsistent, the model compounds that error across future projections.
The reality gap appears when companies invest in advanced forecasting tools but neglect input validation. A machine learning model cannot compensate for flawed pricing or competitive signals. It can only amplify them.
Small inaccuracies in pricing or volume assumptions compound across time periods. A two percent pricing error can distort quarterly revenue projections by millions in high volume categories. These errors affect inventory, marketing spend, and margin planning, creating operational instability beyond finance reporting.
Forecasting models assume input stability. When pricing data is misaligned or competitive benchmarks are outdated, demand elasticity assumptions break.
A pricing update is delayed in the system.
Forecast model assumes higher price point.
Projected revenue appears inflated.
Inventory is ordered based on overstated demand.
Margin compression follows due to reactive discounting.
This is not theoretical.
Situation: A retailer updates prices daily to match competitors.
What breaks without accurate data: Forecasts rely on last week’s price snapshot. Demand sensitivity is miscalculated.
What changes when accuracy improves: Real-time validated price feeds reduce forecast variance by aligning demand assumptions with current market reality.
Strategic takeaway: Competitive pricing data must be continuously monitored, not periodically sampled.
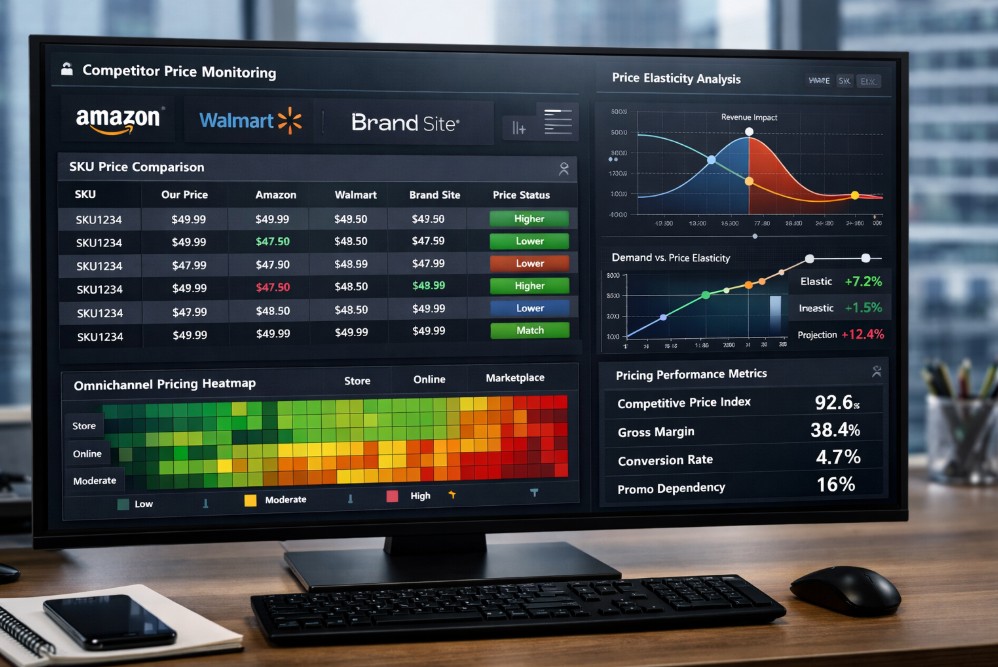
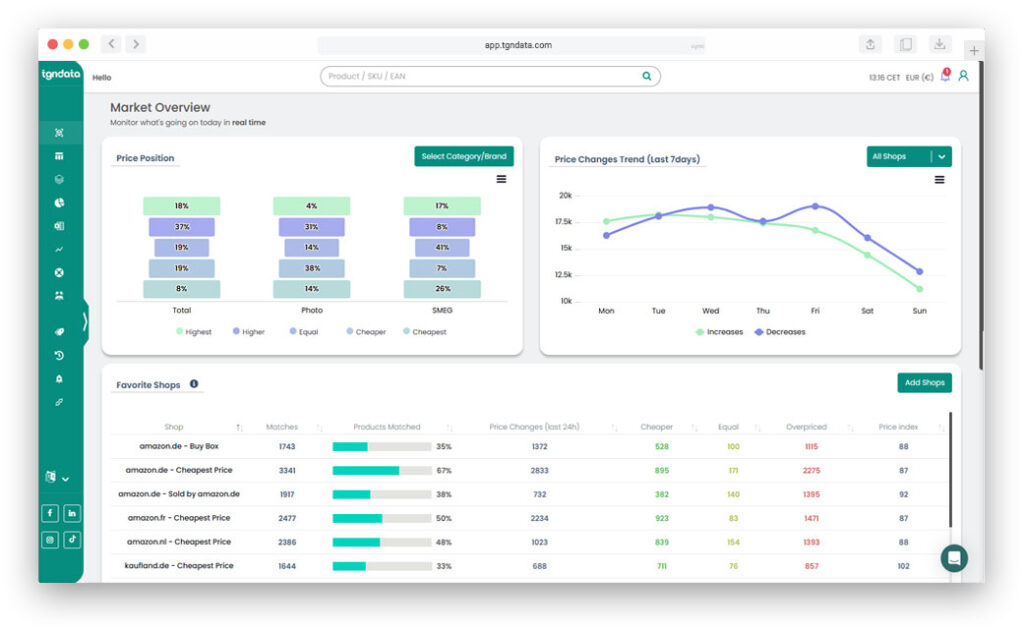
Platforms like tgndata serve as validation layers that ensure competitive pricing inputs are continuously aligned before entering forecasting systems.
Pricing intelligence improves revenue forecasting by validating competitive benchmarks and internal price changes before they influence projections. Accurate pricing inputs reduce forecast volatility, protect margin assumptions, and provide clearer demand elasticity signals for finance and pricing teams.
Forecast accuracy is not just about internal CRM or ERP data. External competitive pricing shifts directly influence demand.
When pricing intelligence is inconsistent:
Elasticity models misfire
Promotional ROI is overstated
Margin forecasts become unstable
Definition: Pricing intelligence is structured monitoring of competitor price movements and promotional behavior.
Reality: Many teams rely on manual scraping or infrequent checks, introducing lag and inconsistencies.
Situation: Brand adjusts prices based on marketplace competition.
What breaks: Competitive promotions are detected late, causing missed price adjustments and inflated forecasts.
What changes: Accurate, automated competitive tracking aligns price reactions with real-time market conditions.
Strategic takeaway: Forecasting stability requires synchronized competitive data feeds.
tgndata functions as an operational backbone that monitors pricing changes continuously, reducing latency between market shifts and forecast updates.
Forecast variance increases when input data lacks consistency and validation. High variance erodes executive confidence and slows decision cycles. Accurate data reduces variance, stabilizes planning, and strengthens trust between finance, pricing, and operations teams.
Variance is not only a financial metric. It is a credibility metric.
CFO confidence declines
Budget approvals tighten
Strategic investments slow
Repeated mid quarter forecast corrections
Unexpected margin compression
Inventory surplus despite optimistic projections
Large discrepancies between regions
Situation: Regional pricing differs by geography.
What breaks: Inconsistent regional data aggregation distorts the national forecast.
What changes: Standardized, validated pricing inputs reduce cross region discrepancies.
Strategic takeaway: Forecast accuracy depends on harmonized data pipelines.
Revenue forecasts often fail before modeling begins due to broken data workflows. Errors occur during collection, transformation, and integration across ERP, CRM, and pricing systems. Strengthening validation and governance at each stage improves overall forecast reliability.
Most organizations focus on forecasting algorithms. Few audit the data pipeline feeding them.
Manual data entry leads to formatting inconsistencies.
ETL pipelines transform incomplete records.
BI dashboards surface inaccurate summaries.
Forecast model consumes distorted aggregates.
Situation: Seller integrates marketplace APIs manually.
What breaks: Inconsistent product identifiers cause pricing mismatches.
What changes: Automated validation reduces duplication and aligns SKUs across systems.
Strategic takeaway: Data governance precedes forecasting sophistication.
tgndata integrates into existing workflows via API, acting as a monitoring system that flags anomalies before they influence projections.
AI forecasting models amplify input quality. When data accuracy improves, machine learning models generate more stable and precise revenue projections. When data quality is poor, AI systems accelerate forecast errors at scale, increasing financial risk.
Machine learning models rely on pattern detection.
If pricing data fluctuates due to input inconsistencies rather than market reality, the algorithm misinterprets noise as trend.
Situation: Dynamic pricing experiments run weekly.
What breaks: Inconsistent logging of discount depth skews model training.
What changes: Clean, structured inputs improve predictive reliability.
Strategic takeaway: AI forecasting requires disciplined data validation before experimentation.
This is where organizations see exponential returns from investing in accuracy rather than additional modeling complexity.
A trusted forecasting system combines validated pricing data, harmonized workflows, competitive intelligence, and continuous monitoring. Executive confidence increases when forecast variance declines and margin projections align with actual performance. Data accuracy becomes a strategic asset rather than an operational afterthought.
Embedded real world narrative:
Companies that treat pricing data as a strategic asset outperform those treating it as a reporting output.
Leadership confidence grows when:
Forecast adjustments decrease
Margin variance narrows
Competitive reactions are proactive
Revenue projections align with inventory reality
Data accuracy is not a technical hygiene metric. It is a revenue stabilizer.
Data accuracy directly affects forecast accuracy percentage because reliable inputs reduce variance between projected and actual revenue. Accurate pricing, volume, and competitive signals stabilize demand assumptions, leading to more consistent projections across reporting periods.
Yes. Even small pricing errors compound across high volume transactions and multiple periods. A minor percentage misalignment can significantly distort projected revenue and gross margin, especially in competitive or price sensitive categories.
AI models fail when input data is inconsistent, incomplete, or delayed. Machine learning amplifies input patterns, so flawed data produces amplified forecasting errors. Clean, validated data is essential for model reliability.
Competitive pricing data influences demand elasticity and promotional response assumptions. Without accurate competitive benchmarks, revenue projections may overestimate demand or underestimate margin pressure.
Companies can reduce forecast variance by implementing data validation processes, monitoring competitive pricing continuously, integrating systems via API, and standardizing SKU level data governance.
It depends on resources and scale. Building offers control but requires significant engineering investment. Buying specialized pricing intelligence tools provides faster deployment and validated external data. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach.
Understanding how data accuracy impacts revenue forecasting changes how organizations prioritize analytics investments.
The greatest gains rarely come from new algorithms. They come from validated pricing inputs, competitive monitoring, and disciplined data governance.
tgndata supports pricing and revenue teams as an enabler and validation layer that strengthens forecast stability before projections reach the CFO dashboard.
If your organization is experiencing forecast variance, margin compression, or pricing inconsistencies, the starting point is not a new model. It is a data accuracy diagnostic.
At a strategic level, how data accuracy impacts revenue forecasting determines whether projections become a competitive advantage or a recurring liability. Organizations that prioritize validated pricing and competitive inputs consistently outperform those relying on delayed or fragmented data streams.





We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!