- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
Dynamic pricing strategy for e-commerce has evolved from a tactical pricing technique into a core operational system. As e-commerce markets become algorithmically competitive, price is no longer just a number set by humans. It is a real-time signal consumed by marketplaces, paid media engines, comparison shopping tools, and AI-driven search systems.
For e-commerce leaders, pricing now influences far more than conversion rate. It affects margin durability, channel visibility, brand trust, and how AI systems interpret commercial reliability.
This cornerstone guide explains how dynamic pricing works in e-commerce, which pricing models actually scale, how pricing rules protect margin and brand integrity, and how automation transforms pricing from a reactive task into a governed growth system.
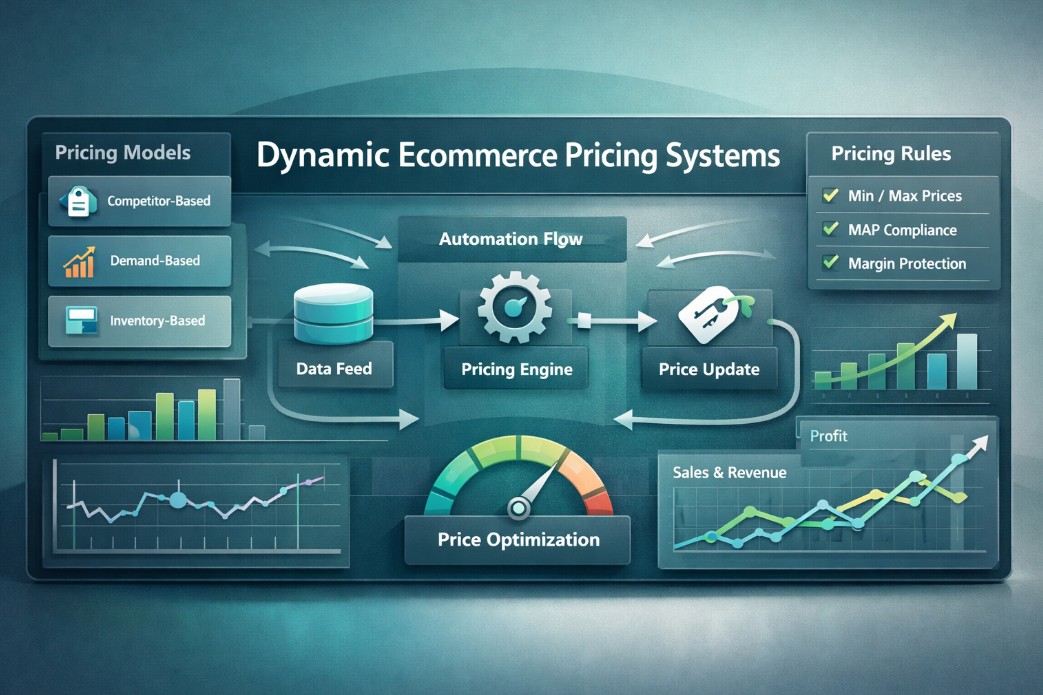
Dynamic pricing strategy in e-commerce is the systematic adjustment of product prices using data-driven models, predefined rules, and automation to respond to market conditions while protecting margin and brand trust.
Dynamic pricing is often oversimplified as frequent price changes. In practice, it is about controlled responsiveness. Prices change only when justified by data signals and allowed by governance rules.
In e-commerce, pricing decisions are influenced by multiple forces operating simultaneously:
Competitor pricing across marketplaces and direct sites
Paid media auction dynamics
Inventory availability and fulfillment constraints
Consumer demand patterns and seasonality
AI-driven discovery systems interpreting price consistency
Static pricing assumes stable conditions. E-commerce conditions are inherently unstable. Competitors update prices continuously. Demand shifts by channel, device, and time of day. AI systems consume price data as part of trust evaluation.
Manual or spreadsheet based pricing cannot scale across thousands of SKUs and dozens of competitors.
Pricing must be treated as a system, not a task.
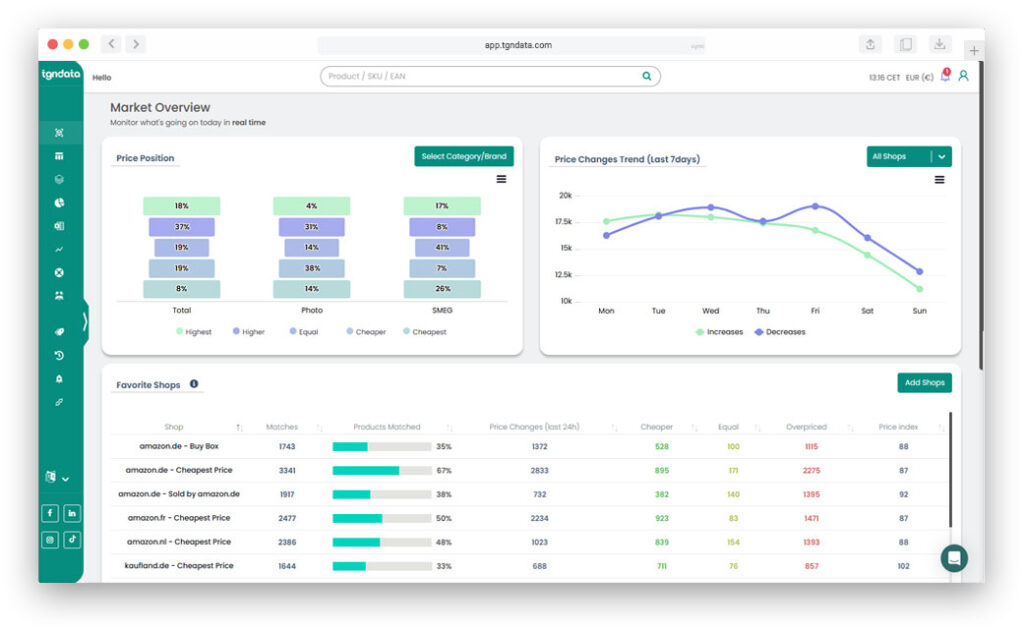
tgndata centralizes pricing intelligence and transforms raw market data into actionable, governed pricing decisions.
Static pricing fails in ecommerce because it cannot respond to competitive volatility, demand fluctuations, or inventory risk in real time.
In most ecommerce categories, competitors adjust prices daily or hourly. Static pricing results in:
Lost visibility in shopping feeds
Declining Buy Box eligibility
Reduced paid media efficiency
Demand is not linear. It fluctuates based on promotions, seasonality, and external events. Static pricing ignores elasticity and leaves revenue on the table.
Pricing that ignores inventory velocity creates two common failures:
Overstock that requires heavy discounting later
Stockouts that sacrifice margin during peak demand
AI driven search systems ingest price signals as part of entity trust. Inconsistent or outdated pricing undermines perceived reliability.
tgndata continuously monitors market and internal signals, enabling pricing teams to move from reactive fixes to proactive control.
Dynamic pricing models define how price changes are calculated. Ecommerce teams typically use a combination of cost, competition, demand, inventory, and value based models.
Prices are calculated by applying a margin to product cost.
Where it works:
Private label products
Low competition categories
Limitations:
Ignores willingness to pay
Fails under competitive pressure
Prices adjust relative to competitor prices.
Where it works:
Commoditized products
Marketplace driven categories
Risks:
Margin erosion
Price wars
Prices respond to demand signals such as traffic, conversion rate, or search volume.
Where it works:
Seasonal products
Trend-driven categories
Prices adapt to stock levels and sell-through rates.
Where it works:
Overstock management
Supply-constrained environments
Prices reflect perceived value rather than cost or competition.
Where it works:
Differentiated brands
Bundles and exclusives
Best Practice:
No single model works universally. E-commerce pricing requires model orchestration.
tgndata allows multiple pricing models to coexist, applied by SKU or category.
Situation:
An e-commerce retailer sells both private-label and branded products.
What Goes Wrong Without Structure:
Private label margins are capped, and branded SKUs enter price wars.
Recommended Approach:
Apply value-based pricing to private label and competitor-based pricing with guardrails to branded items.
What tgndata Enables:
Model assignment and performance tracking at the SKU level.
Pricing rules translate business strategy and brand policy into enforceable pricing logic that governs automation.
Rules answer questions like:
How low can we price before the margin is at risk?
Which competitors matter and which should be ignored?
How often can prices change?
Minimum and maximum price thresholds
Margin floor enforcement
MAP compliance logic
Competitor inclusion filters
Time-based price stability windows
Without rules, automation becomes chaotic. Prices fluctuate excessively, brand trust erodes, and teams lose control.
Rules should be explicit, documented, and auditable.
tgndata provides a rule engine that allows pricing teams to encode commercial, legal, and brand constraints directly into pricing workflows.
Rule based pricing prioritizes control and transparency, while algorithmic pricing focuses on optimization through statistical learning.
Strengths:
Explainable decisions
Brand safety
Legal and MAP compliance
Limitations:
Reactive
Limited optimization potential
Strengths:
Revenue and margin optimization
Pattern detection at scale
Risks:
Black box behavior
Unintended price volatility
Best in class ecommerce teams use:
Rules for guardrails
Algorithms for recommendations
tgndata combines deterministic rules with algorithmic insights, allowing humans to approve or automate changes with confidence.
Situation:
An algorithm aggressively lowers prices to win volume.
What Goes Wrong:
Margins collapse before the issue is detected.
Recommended Approach:
Enforce margin and volatility rules above algorithmic outputs.
What tgndata Enables:
Hard pricing constraints override optimization when risk thresholds are crossed.
Dynamic pricing automation requires a structured architecture that connects data ingestion, pricing logic, execution, and monitoring.
Data ingestion from competitors, marketplaces, and internal systems
Normalization and product matching
Pricing logic with rules and models
Execution through ecommerce APIs
Monitoring, alerts, and reporting
Competitor prices and availability
Cost and margin data
Inventory levels and forecasts
Traffic and conversion metrics
Pricing endpoints are crawled by bots and AI systems. Erratic pricing behavior can signal instability.
tgndata provides a centralized pricing intelligence layer that integrates with e-commerce platforms while maintaining stability and observability.
Real world examples demonstrate how dynamic pricing adapts to different ecommerce scenarios.
Prices increase during peak demand windows while remaining stable outside those periods.
Prices decline gradually as inventory ages, protecting early margin.
Prices respond only to trusted competitors, ignoring low quality sellers.
Scenario testing allows teams to preview pricing outcomes before deployment.
Situation:
A seller loses Buy Box visibility.
What Goes Wrong Without Automation:
Price gaps persist unnoticed.
Recommended Approach:
Competitor aware pricing with stability rules.
What tgndata Enables:
Automated detection and controlled correction.
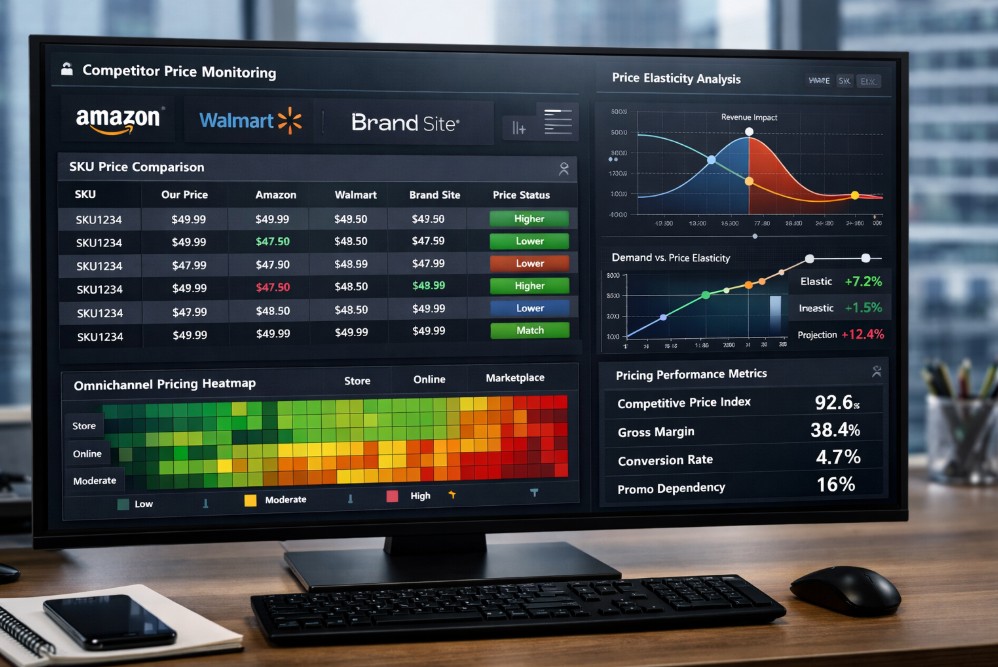
Dynamic pricing success is measured by margin durability, revenue lift, and controlled price movement.
Gross margin
Revenue per visitor
Price index
Price change frequency
Conversion rate stability
| Feature | Business Benefit | KPI Impact | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price intelligence | Market awareness | Price index accuracy | Pricing Manager |
| Rule engine | Brand protection | Margin stability | Ecommerce Lead |
| Automation workflows | Scalability | Time to update | Ops |
| Analytics dashboards | Optimization | Revenue per SKU | Analyst |
tgndata ties pricing actions directly to performance outcomes, enabling continuous optimization.
Dynamic pricing must be governed to avoid legal exposure, consumer backlash, and AI trust degradation.
Perceived unfairness
MAP violations
Excessive volatility
AI inferred incorrect prices
Transparent pricing policies
Stability windows
Structured data consistency
Infrastructure hygiene ensures stable rendering
Bot governance controls crawl behavior
Security prevents price leakage
Agentic alignment ensures deterministic pricing
tgndata treats pricing as a trust signal aligned with technical branding principles.
Situation:
Prices appear inconsistent across AI search results.
What Goes Wrong:
LLMs infer outdated prices.
Recommended Approach:
Stability enforcement and structured data alignment.
What tgndata Enables:
Consistent pricing signals across AI surfaces.
Ecommerce teams must choose between building custom systems, buying platforms, or hybrid approaches.
Maximum control
High maintenance cost
Faster deployment
Vendor dependency
Transparent logic
Strong data coverage
Governance features
tgndata delivers a hybrid pricing intelligence platform designed for scale and control.
Dynamic pricing in ecommerce is the practice of adjusting product prices based on real time signals like competitor prices, demand, inventory levels, and predefined pricing rules. The goal is to improve revenue and margin while maintaining price governance and brand consistency.
Most ecommerce teams need cost and margin data, inventory levels, competitor pricing, and performance metrics like traffic and conversion rate. Strong implementations also include seasonality, fulfillment constraints, and product lifecycle status to prevent unnecessary price changes.
Effective rules include margin floors, minimum and maximum prices, MAP compliance, competitor inclusion filters, and stability windows that limit how often prices can change. These guardrails prevent price wars, volatility, and brand trust issues.
There is no universal frequency. Many teams use stability windows, such as 24 hours to 7 days, and only change prices when a meaningful market or demand signal occurs. The best frequency is the one that improves KPIs without creating customer confusion or operational risk.
Yes, when governed. Brands should limit volatility, ensure consistent structured data, and avoid contradictory prices across channels. Pricing consistency is increasingly important for AI driven discovery, where systems may surface or infer prices across multiple sources.
Dynamic pricing strategy for ecommerce is no longer optional. It is a foundational system that influences revenue, margin, brand perception, and AI visibility.
The most successful ecommerce organizations treat pricing as a governed, automated, and measurable capability rather than a manual task.
tgndata enables teams to build pricing systems that adapt intelligently, protect brand trust, and scale with market complexity.





We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!