- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
Predictive pricing helps retailers move from reactive decision making to proactive strategy. Instead of waiting for competitors to change prices or launch promotions, predictive pricing uses historical pricing data to forecast what competitors will do next. This allows pricing teams to anticipate market moves, prepare strategic responses and improve margin stability. Predictive pricing transforms historical data into a forward looking intelligence layer that guides pricing decisions with accuracy and confidence.

Predictive pricing uses analytical models to forecast future pricing events. These forecasts include expected competitor price changes, promotional activity, discount depth, price index shifts and seasonal pricing cycles. The goal is to anticipate change before it occurs, so pricing teams can position themselves strategically.
Anticipating competitor movements gives retailers a strategic advantage. When a competitor is likely to launch a promotion, predictive pricing helps teams prepare either to match it or differentiate with a smarter alternative. Anticipation reduces disruption, improves consistency and increases ability to protect long term margin. Retailers that rely only on reactive changes often find themselves in price wars or repeated last minute decisions.
Traditional pricing relies heavily on static rules and historical averages. Predictive pricing introduces a dynamic approach where decisions evolve with market expectations. This shift helps retailers respond to competitive pressure with more precision. Instead of using generic strategies, teams adjust based on what the model forecasts competitors will do.
Machine learning strengthens predictive pricing by detecting patterns humans may not see. Models evaluate historical movements, category cycles, competitor habits and external signals. They identify correlations and triggers that influence pricing decisions. This improves the accuracy of competitor forecasting and reduces uncertainty.
Historical pricing data captures the full behavior of competitors over time. This data includes every price change, discount, promotion, stock-driven adjustment, and category-specific pattern. Predictive pricing relies on these behavioral timelines to understand how competitors behave in similar conditions.
Competitors follow habits even when the market appears unpredictable. Historical pricing data reveals how often competitors change prices, which discount depths they prefer and how responsive they are to market pressure. These patterns become the basis for forecasting future decisions.
Historical pricing data provides clarity around seasonal and cyclical events. Predictive models use past seasonal activities to anticipate when competitors will launch promotions. For example, electronics retailers show predictable cycles during Black Friday, back to school and product launch seasons.
Historical data exposes the triggers that cause competitors to adjust price. These triggers may include stock movements, promotional timing, competitor undercutting or demand spikes. Predictive models use these triggers to anticipate when competitors will take action.
Historical data helps establish baseline performance benchmarks. These baselines show what normal pricing behavior looks like and when deviations may signal upcoming competitor moves. Threshold detection helps models identify when competitors are likely to react.
Predictive pricing models rely on multiple data sources that reflect competitor behavior and market conditions.
These include all list price changes, competitive price adjustments and promotional price variations. Historical price points form the backbone of predictive pricing analysis.
Promotional history includes discount depth, duration, event type and timing. Predictive models use this data to detect promotional cycles and forecast future discount behavior.
Competitors respond to stock conditions. Overstock triggers aggressive discounting, while stockouts reduce the need for immediate price competition. Availability signals help forecast when competitors are likely to drop prices.
Markets show clearer competitive patterns because products are frequently repriced by seller algorithms. Models use buy box trends, seller counts and price clustering to forecast movement.
Category demand metrics reveal when customers are most sensitive to price changes. When demand is weak or strong, predictive pricing adjusts forecasts accordingly.
Inflation rates, consumer confidence and economic shifts influence how competitors price products. Predictive models integrate these factors for improved accuracy.
Competitors follow pricing patterns even if they seem unpredictable. These patterns become clearer when analyzing long term data.
Some competitors adjust prices daily, while others adjust weekly or monthly. Predictive pricing identifies these frequencies to forecast when adjustments will occur.
Competitors often rely on specific discount levels. Historical data shows whether a retailer prefers shallow discounts like five percent or more aggressive options like twenty percent.
Promotional cadence describes how often competitors run promotions. Many retailers have predictable schedules aligned with pay cycles, holidays or category milestones.
Some competitors react quickly to pricing changes from others, while others are slow movers. Predictive pricing models these reaction times to anticipate when competitors will respond.
Competitors often aim to maintain specific price gaps relative to top-tier retailers. Predictive models track these index strategies and forecast future adjustments.
Predictive pricing uses advanced modeling techniques to forecast competitor behavior. These models analyze historical patterns and forward looking signals.
Time series models such as ARIMA, Holt Winters and Prophet analyze historical price movements to detect seasonality and trends. They predict when competitors are likely to adjust pricing based on repeated patterns.
Regression models such as random forests and gradient boosting evaluate relationships between features like demand, stock levels, competitor pricing and discount history. These models provide robust forecasts and adapt to new data.
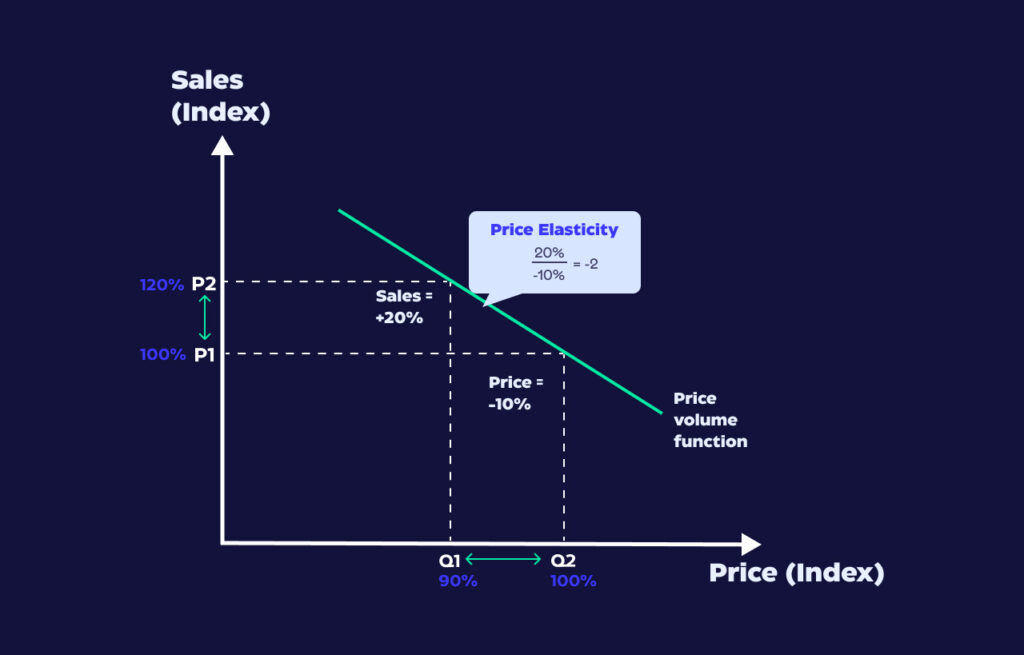
Elasticity models measure customer response to price changes. Predictive pricing uses elasticity insights to forecast when competitors will adjust prices due to demand shifts.
These models classify whether a competitor is likely to run a promotion in a given period. They use historical promotional cycles, demand conditions and category events.
Event driven models identify triggers such as seasonal demand spikes, stock buildup or steep competitive undercutting. These models predict when such triggers will cause price adjustments.
Competitors influence each other. Multi competitor models simulate how one competitor’s action affects others. This improves predictive accuracy in dense markets.
Seasonality and promotional cycles are essential components of predictive pricing. Historical data reveals when competitors are most likely to offer discounts or modify pricing.
Seasonal pricing patterns repeat annually. Predictive pricing identifies when these cycles start and end, helping retailers time their strategies effectively.
Some competitors launch promotions early to capture early demand. Others wait until the last minute to maximize urgency. Predictive models forecast lead times based on past behavior.
Categories like electronics, sporting goods and fashion show sharp seasonal cycles. Predictive models adjust forecasts based on category specific timing.
Seasonal peaks accelerate competitive tension. Predictive pricing identifies which competitors are likely to move first and which follow after market activity increases.
Competitors react to market conditions in measurable ways. Historical pricing data helps identify these reaction thresholds.
Each competitor has sensitivity points that trigger a response. Some react when market price gaps widen beyond specific percentages. Predictive pricing identifies these thresholds to forecast changes.
Market leaders set the tone for pricing. Smaller competitors often adjust their prices based on leader movements. Predictive models reveal how closely competitors follow leaders.
Competitors often discount when inventory builds up or when demand slows. Predictive models use these signals to anticipate pricing activity.
Some competitors adjust pricing to protect margin rather than follow market pressure. Predictive models detect when margin preservation drives pricing decisions.
Predictive pricing also identifies the strategic mindset behind competitor pricing decisions.
Retailers with everyday low pricing maintain consistent price levels. Predictive pricing shows minimal volatility but highlights predictable small adjustments.
These competitors maintain high list prices but run frequent deep promotions. Predictive pricing detects promotional cadence and expected discount depths.
Automated competitors reprice frequently based on algorithms. Predictive pricing models incorporate their rapid adjustments and forecasts, likely resulting in price ranges.
Category specialists focus on narrow assortments where they hold deeper expertise and pricing precision. Their pricing behavior often reflects deep understanding of product lifecycles, demand elasticity and brand value within that niche. Predictive pricing identifies how these specialists time promotions, adjust price during product expiry cycles and respond to competitive pressure within their focus area. These competitors often move strategically rather than frequently, making their behavior easier to forecast with accurate historical data.
Real-time pricing intelligence shows what competitors are doing at this moment. Predictive intelligence shows what competitors are likely to do next.
Both are essential for an effective pricing strategy. Real-time data supports immediate reaction, especially during fast-moving promotions, inventory shifts, or algorithmic repricing events.
Predictive intelligence provides the foresight needed for planned promotions, margin protection strategies and long-term pricing decisions.
Real time intelligence captures immediate changes such as sudden price drops, rapid undercutting or buy box competition. This helps pricing teams react quickly to avoid losing visibility or conversion. Real time pricing is critical in marketplaces where prices adjust multiple times per day.
Predictive intelligence goes a step further by guiding strategic planning. It helps teams understand when competitors are likely to run promotions, how deep those promotions may be and whether they will maintain or shift price positions. Predictive models prevent over correction and help teams avoid unnecessary pricing battles.
The strongest pricing strategies use real time and predictive intelligence together. Real time alerts prevent sudden losses, while predictive insights shape long term profitability and competitive readiness. Together, they create a complete pricing intelligence framework.
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices using rules, algorithms and market signals. Predictive pricing adds a foresight layer that enhances dynamic pricing accuracy. Instead of reacting to competitor moves, dynamic pricing systems can anticipate and prepare for future changes.
Predictive pricing forecasts upcoming promotions based on past behavior. Dynamic pricing systems can use these forecasts to adjust positioning early, avoid margin loss or match competitor timing with better targeted offers.
Many retailers overreact to competitor price drops. Predictive models help determine whether a price change is a temporary fluctuation or part of a longer trend. This reduces unnecessary price cuts.
Predictive pricing improves elasticity based pricing by forecasting demand shifts before they occur. This helps dynamic systems adjust price according to future expectations rather than current conditions alone.
Dynamic pricing can be aggressive when reacting to real time changes. Predictive forecasts add guardrails that protect long term margin by guiding more deliberate pricing actions.
A strong predictive pricing workflow requires structured processes, reliable data pipelines and feedback loops that ensure continuous improvement.
Data must be collected consistently and accurately. This includes historical pricing, competitor movements, stock signals, promotional timelines and category dynamics.
Models rely on clean data. Removing outliers, correcting mismatches and aligning timestamps improves accuracy. Data governance ensures consistent model inputs.
Feature engineering transforms raw data into meaningful variables such as price volatility measures, seasonal markers, competitor response speeds and elasticity tiers. These features increase model accuracy.
The development phase includes selecting algorithms, tuning hyperparameters and training models on historical pricing data. Multiple models may run in parallel to determine which offers the best forecast accuracy.
Backtesting evaluates how well the model predicts past pricing behavior. This allows teams to refine inputs, improve detection of pricing triggers and reduce prediction errors.
Predictive outputs must be integrated into dashboards, pricing tools or dynamic pricing engines. This ensures insights translate into practical pricing decisions.
Predictive models must evolve with new data. Regular refresh cycles ensure they continue learning from shifting market conditions, competitor strategy changes and category developments.
Predictive pricing is only as strong as the data it relies on. Operational issues can weaken forecast accuracy and reduce the value of predictive insights.
Gaps in historical pricing data reduce the ability to detect long term patterns. Retailers must ensure full price histories are captured for all relevant competitors.
Incorrect product matching can distort pricing signals. Ensuring accurate product mapping across retailers is essential for reliable predictions.
Competitor price changes must be recorded consistently. Timestamp inconsistencies create false signals that reduce model accuracy.
If promotions are not labeled correctly, models cannot learn from past promotional cycles. Clean labeling improves forecasting precision.
Ignoring category specific behavior reduces model relevance. Predictive pricing must integrate category level features to remain accurate.
Predictive pricing supports strategic decisions across multiple retail and ecommerce sectors.
Electronics experience frequent promotions and price volatility. Predictive pricing helps retailers anticipate competitor launches, price drops and lifecycle driven markdowns.
Fashion follows strong seasonal trends. Predictive pricing identifies promotional cycles, new collection timing and end of season markdown behavior.
Grocery relies on repeated promotional cycles linked to loyalty behavior. Predictive pricing improves promotion timing and depth across staples and high velocity items.
Home improvement categories are influenced by seasonality and project cycles. Predictive pricing forecasts competitive activity during key periods such as spring renovation season.
Promotional bursts are common in beauty. Predictive pricing anticipates competitor launches, exclusive events and discount waves.
Predictive pricing transforms historical pricing data into actionable foresight. By identifying competitor behavior patterns, forecasting promotional cycles and detecting reaction thresholds, pricing teams can anticipate competitor moves before they occur. Predictive models help retailers plan strategically, protect margin, optimize positioning and strengthen competitive advantage.
If your organization is ready to apply predictive pricing using accurate historical pricing data, tgndata delivers the intelligence, automation and analytics foundation you need. Connect with tgndata to unlock predictive insights and anticipate competitor moves with clarity and confidence.




We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!