- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
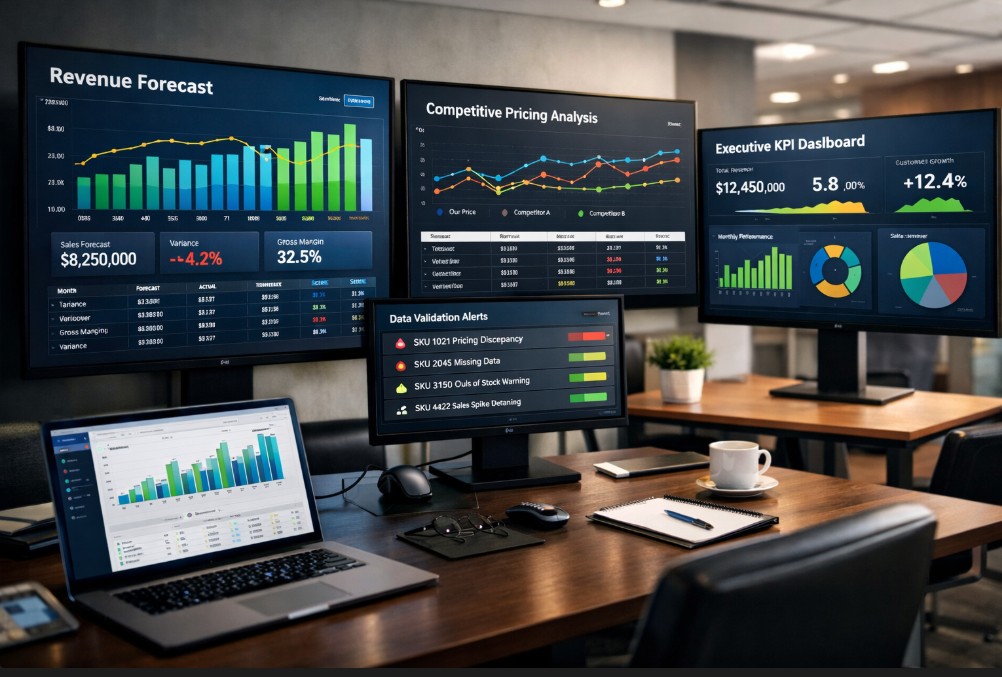
Dynamic Pricing Software vs Manual Repricing is one of the most critical decisions modern retail and ecommerce teams face. Pricing directly impacts revenue, margins, brand perception, and competitiveness. As product assortments expand and competitors react faster, pricing models that once worked begin to break under operational pressure.
This guide explores how manual repricing compares to dynamic pricing software, not just in theory, but in real operational conditions. It covers cost, scalability, risk, governance, and how pricing decisions increasingly act as brand signals in AI driven search environments.

Pricing used to be a quarterly or monthly exercise. Today, it is continuous. Marketplaces update prices multiple times per day. Consumers compare prices instantly. AI search engines interpret pricing consistency as a trust signal.
Manual repricing struggles under these conditions. Dynamic pricing software promises automation, speed, and data driven decisions, but it introduces new questions around control, governance, and brand safety.
This comparison breaks down where each approach works, where it fails, and how to choose a pricing model aligned with growth, margins, and long term brand authority.
Manual repricing is the process of reviewing and adjusting prices by hand using spreadsheets, dashboards, or ecommerce admin tools. Decisions are made periodically based on limited data and human judgment rather than continuous automated rules.
Manual repricing typically involves exporting competitor prices, reviewing margins, checking inventory, and updating prices one SKU at a time. It is still widely used by small retailers and niche brands.
Most teams rely on:
Spreadsheet based price lists
Periodic competitor checks
Fixed markup or margin rules
Human approval cycles
The process is familiar and feels controlled. Pricing managers can explain every decision because they made it manually.
Manual repricing creates an illusion of precision. In reality:
Data is outdated as soon as it is reviewed
Errors scale with SKU count
Teams spend time executing instead of analyzing
tgndata allows teams to retain manual oversight while automating execution. Rules, alerts, and approvals replace repetitive spreadsheet work without removing human judgment.
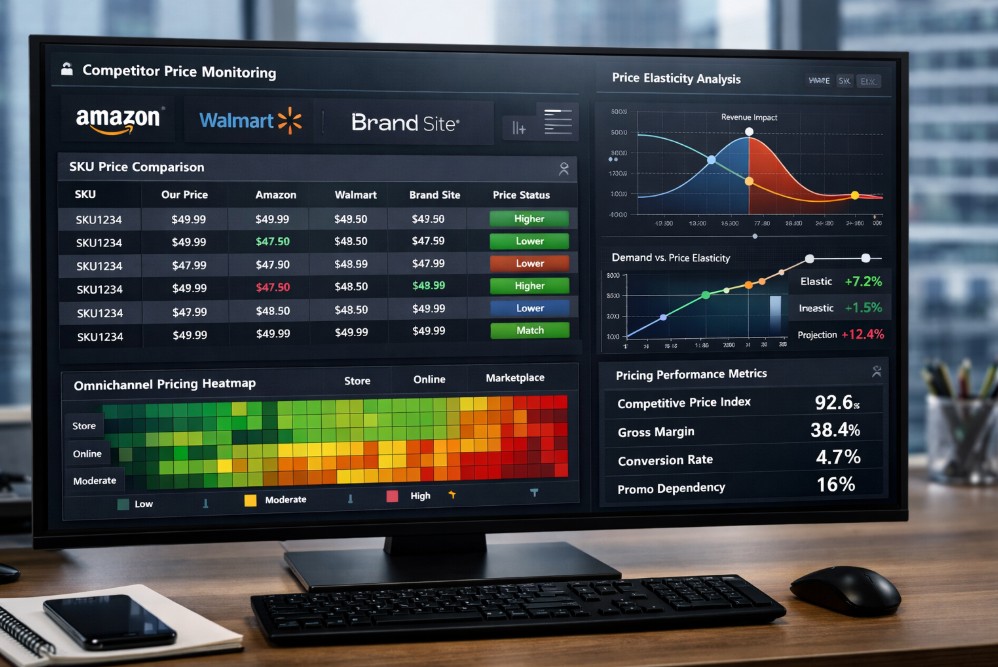
Dynamic pricing software automatically adjusts prices based on predefined rules, real time data, and market signals such as competitor pricing, demand, and inventory levels.
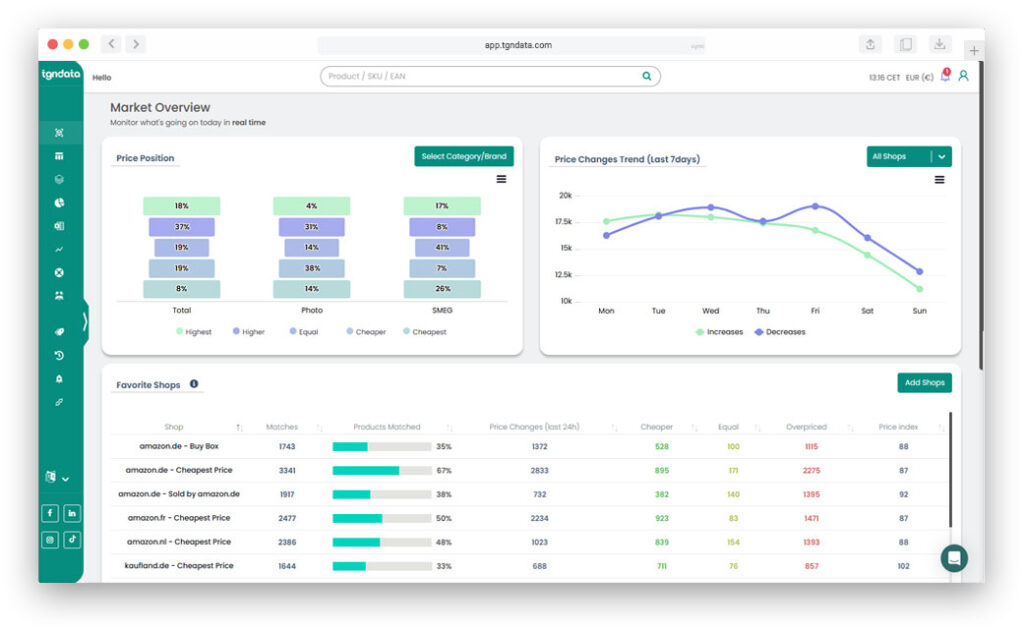
Dynamic pricing systems continuously ingest data and apply pricing logic at scale. Instead of reviewing each SKU, teams manage pricing strategy through rules and thresholds.
Dynamic pricing platforms typically include:
Rule based pricing engines
Margin and cost constraints
Demand and inventory signals
Automated publishing to channels
Automation shifts pricing from execution to strategy.
As SKU counts grow and markets accelerate, manual repricing cannot keep up. Automation ensures prices reflect current conditions, not last week’s spreadsheet.
tgndata combines automated repricing with analytics and governance layers, ensuring pricing actions are explainable, auditable, and aligned with brand strategy.
Manual repricing prioritizes human judgment but sacrifices speed and consistency. Dynamic pricing software prioritizes speed and accuracy at scale while relying on predefined logic rather than intuition.
Manual pricing decisions may be thoughtful, but they are slow. Automation reacts instantly but requires careful configuration.
Competitors that update prices daily or hourly capture demand shifts faster. Manual workflows often lag behind market changes.
Humans make fewer errors per SKU, but systems make fewer errors across thousands of SKUs. At scale, consistency matters more than perfection.
tgndata enables hybrid models where automation executes fast, while alerts flag exceptions for human review.
Manual repricing appears cheaper upfront but becomes more expensive as SKU counts grow. Dynamic pricing software replaces repetitive labor with predictable software costs.
Manual pricing costs hide in salaries, overtime, and opportunity cost. Pricing teams spend hours updating prices instead of analyzing performance.
Manual repricing costs include:
Analyst and manager time
Error correction
Delayed market response
Dynamic pricing costs include:
Software subscription
Implementation and configuration
Most retailers reach a break even point when SKU counts exceed a few hundred or competitor prices change daily.
tgndata pricing automation reduces execution time.
Situation:
A boutique ecommerce brand with 50 SKUs and stable competitors.
What goes wrong without automation:
Manual pricing consumes time but does not create errors.
Recommended approach:
Manual repricing with structured rules.
What tgndata enables:
Rule templates and alerts prepare the brand for future automation without forcing premature complexity.
Manual repricing does not scale linearly. Each additional SKU increases workload. Dynamic pricing software scales through rules, not labor.
As assortments grow, pricing decisions multiply. Manual workflows break under volume.
Automation does not mean losing oversight. It means defining strategy once and applying it consistently.
tgndata allows pricing logic to scale across categories, brands, and regions with centralized governance.
Manual repricing risks human error and delayed corrections. Dynamic pricing software risks misconfigured rules but reduces random mistakes.
Errors in pricing can damage margins and brand trust.
Manual risks:
Typographical errors
Missed competitor changes
Automation risks:
Incorrect rule logic
Over aggressive pricing
Situation:
A marketplace seller competing with hundreds of sellers.
What goes wrong without automation:
Prices become uncompetitive within hours.
Recommended approach:
Dynamic pricing with competitor monitoring.
What tgndata enables:
Real-time repricing rules aligned with marketplace constraints and margin floors.
Dynamic pricing must be governed to avoid brand damage. Manual pricing is explainable by default but lacks consistency.
As pricing becomes automated, explainability matters. Teams must understand why prices changed.
The best pricing systems include:
Rule documentation
Audit trails
Approval workflows
tgndata emphasizes explainable pricing decisions with full audit logs and governance controls.
Situation:
Prices differ across channels.
What goes wrong without automation:
Inconsistent pricing confuses customers.
Recommended approach:
Centralized dynamic pricing with channel rules.
What tgndata enables:
Channel-aware pricing logic with governance controls.
Building pricing systems offers control but requires significant resources. Buying accelerates time to value. Hybrid approaches balance customization and speed.
Consider:
Team expertise
Time to market
Maintenance cost
tgndata offers configurable automation without requiring full custom development.
| Feature | Business Benefit | KPI Impact | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated repricing rules | Faster response | Revenue lift | Pricing Manager |
| Competitor monitoring | Market awareness | Win rate | eCommerce Analyst |
| Margin floors | Profit protection | Margin % | Finance |
| Alerts and audits | Risk reduction | Error rate | Pricing Lead |
Manual repricing remains viable for small assortments, regulated categories, or brands prioritizing handcrafted pricing strategy.
Manual pricing is not obsolete. It is contextual.
Many teams start manual and layer automation gradually.
Situation:
Strict pricing rules.
What goes wrong without automation:
Compliance errors.
Recommended approach:
Rule-constrained automation.
What tgndata enables:
Compliance-aware pricing logic.
Dynamic pricing software automatically updates prices using rules and data signals like competitor prices, demand, and inventory. Manual repricing relies on people reviewing data and changing prices periodically, which is slower and harder to scale.
Manual repricing typically breaks down when SKU counts grow into the hundreds or thousands, competitors change prices daily, or multiple sales channels must stay aligned. At that point, delays, errors, and inconsistent margin control become common.
It can protect margins when configured with guardrails like cost based floors, margin thresholds, and competitor match limits. “Race to the bottom” usually happens when teams automate without governance, clear rules, or exception handling.
Use pricing rules that are documented, auditable, and tested. Add approval workflows for high impact changes, set alerts for anomalies, maintain rollback options, and track every price change with a reason code tied to the triggering signal.
Rule based systems are easier to control, audit, and roll out quickly. AI based systems can adapt to complex patterns but need strong data quality, monitoring, and governance. Many retailers start rule based and add AI signals gradually.
Dynamic Pricing Software vs Manual Repricing is not a binary choice, but a maturity journey that depends on scale, competition, and pricing governance. Manual repricing offers control and simplicity. Dynamic pricing software offers scale, speed, and consistency.
The most successful teams adopt automation with governance. They use systems to execute and humans to strategize.
tgndata enables this balance by combining pricing automation, analytics, and technical branding. Pricing becomes not just a number, but a controlled signal that drives revenue, trust, and long term competitiveness.





We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!