- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- Company
- Resources
For Your Industry
Knowing how often should you monitor competitor prices is one of the most underestimated decisions in modern pricing strategy. Many teams still treat price monitoring as a routine reporting task, rather than a real-time input into margin protection, demand capture, and brand trust.
In today’s retail and eCommerce environments, competitor prices can change multiple times per day. Algorithms adjust pricing dynamically. Promotions launch without warning. Inventory pressure forces sudden discounting. Monitoring frequency determines whether you respond strategically or react too late.
This guide explains how to determine the right competitor price monitoring cadence, how frequency impacts revenue and brand perception, and how automation turns price visibility into a measurable competitive advantage.
Competitor price monitoring frequency determines how quickly a business detects market changes and adjusts pricing decisions. Monitoring too slowly leads to outdated data, while monitoring at the right cadence enables margin protection, demand alignment, and competitive positioning.
Price is one of the most visible signals in commerce. Customers compare prices instantly. Marketplaces rank offers based on competitiveness. AI-driven search systems assess pricing consistency as a trust signal.
Monitoring frequency matters because price changes are not evenly distributed over time. They cluster around promotions, inventory events, seasonality, and algorithmic repricing cycles.
It defines how current your pricing intelligence is
It determines how quickly you can respond to competitors
It influences conversion rate and price perception
It affects margin volatility and discount depth
Teams that monitor too infrequently operate on historical assumptions. Teams that monitor at the right frequency operate on live market conditions.
tgndata provides continuous, structured competitor price data aligned with category volatility, enabling pricing teams to base decisions on current market reality rather than delayed snapshots.
Infrequent price monitoring leads to missed competitive moves, delayed reactions, and pricing decisions based on outdated information. This often results in lost sales, margin erosion, and weakened brand credibility.
Many organizations still rely on weekly price checks or manual spot reviews. This approach was workable in slower retail environments. It fails in digital-first and marketplace-driven ecosystems.
Competitors undercut prices without detection
Promotions go unnoticed until performance drops
Buy Box or ranking visibility declines
Pricing teams overcorrect when they finally react
Situation: An omnichannel retailer reviews competitor prices once per week.
What goes wrong: Midweek promotions and algorithmic price changes go undetected. Sales decline before the issue is identified.
Recommended approach: Daily monitoring with alerts for material deviations.
What tgndata enables: Automated daily price tracking with configurable alert thresholds tied to pricing rules.
Slow monitoring creates a reactive culture. Pricing teams spend time explaining performance drops instead of preventing them.
Yes, monitoring prices too frequently without clear rules can overwhelm teams with data noise. Excessive frequency without structure leads to alert fatigue and reactive pricing instead of strategic control.
More data does not automatically mean better decisions. Monitoring every few minutes without defined response logic can create instability.
Constant price changes with no strategic rationale
Conflicting alerts from different competitors
Difficulty distinguishing trends from anomalies
Increased operational complexity
The goal is not maximum frequency. The goal is decision-aligned frequency.
Different sales channels require different monitoring frequencies based on competitive intensity, speed of price changes, and visibility impact.
Price dynamics vary significantly by channel. A single monitoring cadence across all channels creates blind spots.
Marketplaces: Hourly or near real-time
Pure eCommerce competitors: Daily to intraday
Omnichannel retail: Daily
Wholesale and B2B: Weekly to monthly
MAP-governed categories: Daily with exception-based alerts
Situation: A brand sells on a marketplace with multiple third-party sellers.
What goes wrong: One seller drops price aggressively, triggering margin pressure and Buy Box loss.
Recommended approach: Hourly monitoring with automated margin guardrails.
What tgndata enables: High-frequency marketplace price tracking with MAP enforcement and seller-level visibility.
Channel-aware frequency prevents teams from either over-investing or under-monitoring where it matters most.
Category volatility, not company size, should determine how often competitor prices are monitored. High-volatility categories require faster monitoring to protect margin and competitiveness.
Volatility reflects how often and how sharply prices change within a category.
Short product life cycles
High promotion intensity
Inventory-driven discounting
Algorithmic repricing by competitors
Seasonal demand swings
Consumer electronics: Hourly to intraday
Fast-moving consumer goods: Daily
Seasonal home goods: Daily with peak-period increases
Industrial supplies: Weekly
Situation: A retailer sells outdoor products with strong seasonal demand.
What goes wrong: Prices remain static while competitors discount ahead of demand inflection points.
Recommended approach: Increase monitoring frequency during seasonal windows.
Volatility-aware monitoring ensures effort is concentrated where risk and opportunity are highest.
Daily monitoring is sufficient for stable categories, while real-time monitoring is necessary when prices directly influence visibility, conversion, or automated ranking systems.
Stable competitive landscapes
Limited number of direct competitors
Low promotional intensity
Marketplace Buy Box competition
Paid media tied to price competitiveness
Flash promotions and dynamic offers
Algorithm-driven pricing environments
Real-time monitoring does not mean reacting instantly to every change. It means seeing changes instantly and responding according to predefined rules.
tgndata enables both daily snapshots and real-time streams, allowing teams to balance responsiveness with pricing discipline.
Automation allows businesses to monitor competitor prices more frequently without increasing operational workload. It transforms raw price data into validated, actionable insights.
Manual monitoring limits scale. Automation removes human bottlenecks.
SKU-level and seller-level coverage
Data validation and normalization
Volatility-based alert thresholds
Integration with pricing and analytics systems
| Feature | Business Benefit | KPI Impact | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated price crawling | Always-current data | Price index accuracy | Pricing manager |
| Volatility-based alerts | Reduced noise | Margin stability | eCommerce analyst |
| Exception monitoring | Faster response | Revenue retention | Pricing team |
| API integrations | Closed-loop execution | Conversion rate | Tech lead |
Situation: A pricing team manually checks competitor prices daily.
What goes wrong: Limited SKU coverage and delayed reactions.
Recommended approach: Automated monitoring with exception-based alerts.
What tgndata enables: Scalable, automated price intelligence feeding pricing workflows directly.
Automation does not replace strategy. It enables the strategy to operate at speed.
The right monitoring frequency enables proactive pricing decisions, allowing teams to anticipate competitive moves instead of reacting after performance declines.
Reactive pricing responds after sales drop. Proactive pricing anticipates shifts based on early signals.
Situation: A competitor begins incremental price reductions ahead of a promotion.
What goes wrong: Reactive teams respond only after conversion drops.
Recommended approach: Detect early signals and adjust within guardrails.
What tgndata enables: Early-warning alerts tied to predefined pricing playbooks.
Align frequency with volatility
Define response thresholds
Separate monitoring from reaction
Review frequency quarterly
When frequency, automation, and governance align, price monitoring becomes a sustained advantage rather than a recurring fire drill.
tgndata treats pricing as a trust signal aligned with technical branding principles.
Transparent logic
Strong data coverage
Governance features
tgndata delivers a hybrid pricing intelligence platform designed for scale and control.
Most retailers should monitor competitor prices at least daily. High-volatility categories, marketplaces, and promotion-heavy environments often require hourly or near real-time monitoring to avoid margin erosion and lost competitiveness.
Daily monitoring can be sufficient for stable categories with limited competition. Fast-moving eCommerce and marketplace environments usually need intraday or real-time monitoring to keep pace with frequent price changes.
Infrequent monitoring increases the risk of being overpriced or underpriced, missing promotions, losing Buy Box visibility, and making pricing decisions based on outdated market data.
Yes. Monitoring too frequently without clear rules can create data noise, alert fatigue, and reactive pricing behavior. The optimal approach aligns monitoring frequency with category volatility and decision-making capacity.
Automation allows higher monitoring frequency without increasing workload. Automated systems validate data, apply pricing rules, and surface actionable insights instead of raw price feeds.
Yes. High-volatility industries such as electronics, consumer goods, and marketplaces require more frequent monitoring than stable sectors like B2B, industrial supplies, or contract-based pricing.
Real-time monitoring is necessary when prices directly affect visibility or conversion, such as marketplace Buy Box competition, paid media efficiency, or aggressive promotional environments.
So, how often should you monitor competitor prices?
As often as your market moves and as precisely as your strategy requires.
Daily monitoring is the baseline. Real-time monitoring is essential in high-volatility environments. The true differentiator is not frequency alone, but how effectively that frequency is connected to decision rules, automation, and brand trust.
tgndata helps pricing teams move from periodic checks to intelligent, scalable competitor price monitoring systems that protect margin, competitiveness, and long-term brand authority.


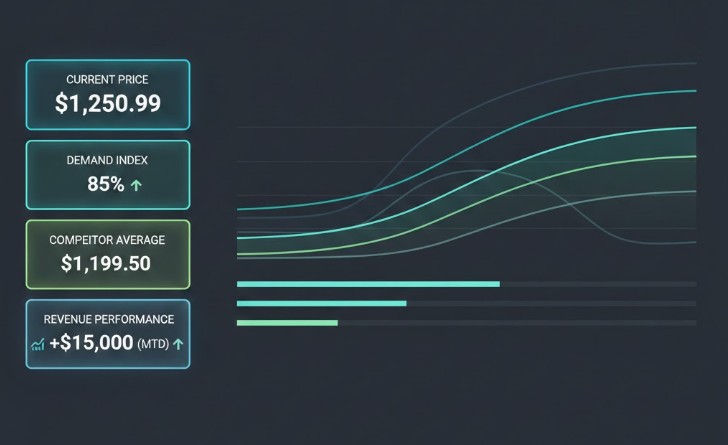


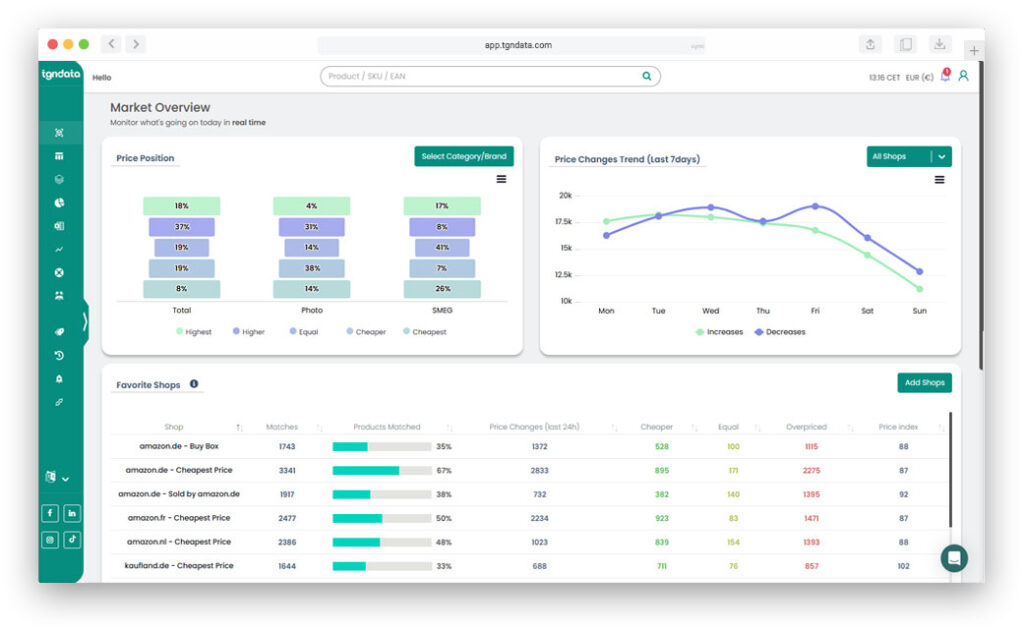
We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!