- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- About us
- Resources
For Your Industry
Pricing decisions are among the fastest moving and highest impact decisions inside a business. Yet they are often made with the least scrutinized data. Most organizations assume pricing data accuracy because the data appears structured, automated, and visually clean. That assumption is where margin erosion begins.
Pricing data accuracy is not about perfection. It is about knowing where your data is strong, where it is weak, and how much decision risk you are willing to accept.

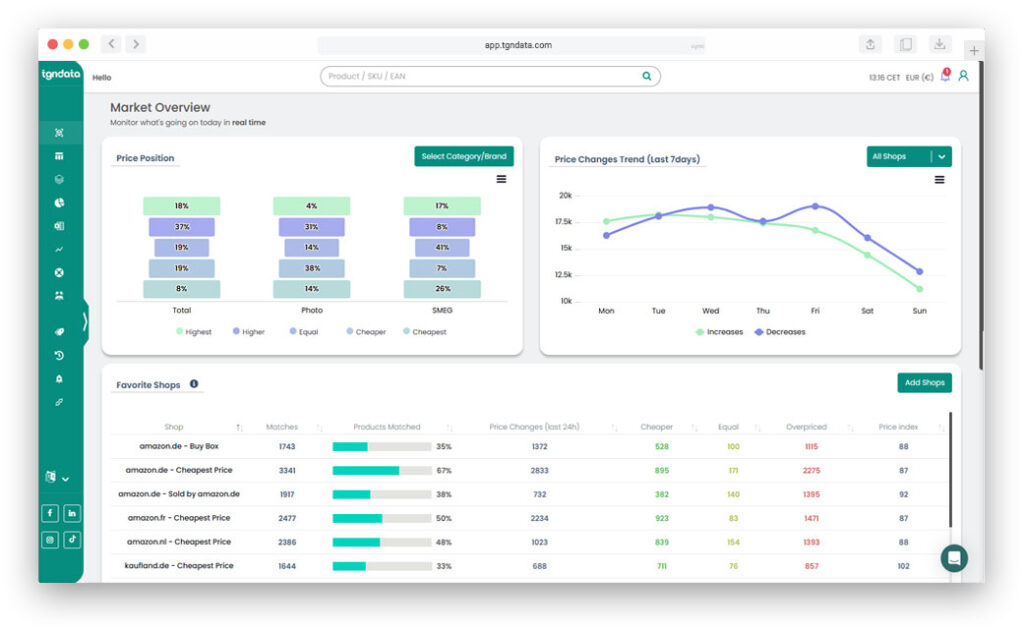
Pricing data accuracy exists on a spectrum. It varies by SKU, retailer, update frequency, and use case. Data can be accurate enough for reporting but unreliable for automated pricing decisions, which creates hidden risk when one dataset is used for everything.
Accuracy changes depending on context. A weekly competitor benchmark does not require the same precision as a real time repricing engine. A MAP compliance check needs exact seller attribution, while assortment strategy needs broad coverage.
The reality gap appears when teams treat pricing data as universally reliable. In practice, accuracy fluctuates by:
Product complexity
Retailer behavior
Promotional frequency
Data collection method
False confidence forms when dashboards present clean averages that hide underlying volatility.
Situation: A consumer electronics brand expanded monitoring from 12 to 60 retailers.
What breaks: SKU matching confidence dropped without being visible.
What changes: Confidence scoring exposed where data should not trigger price actions.
Strategic takeaway: Accuracy and transparency matter more than raw coverage.
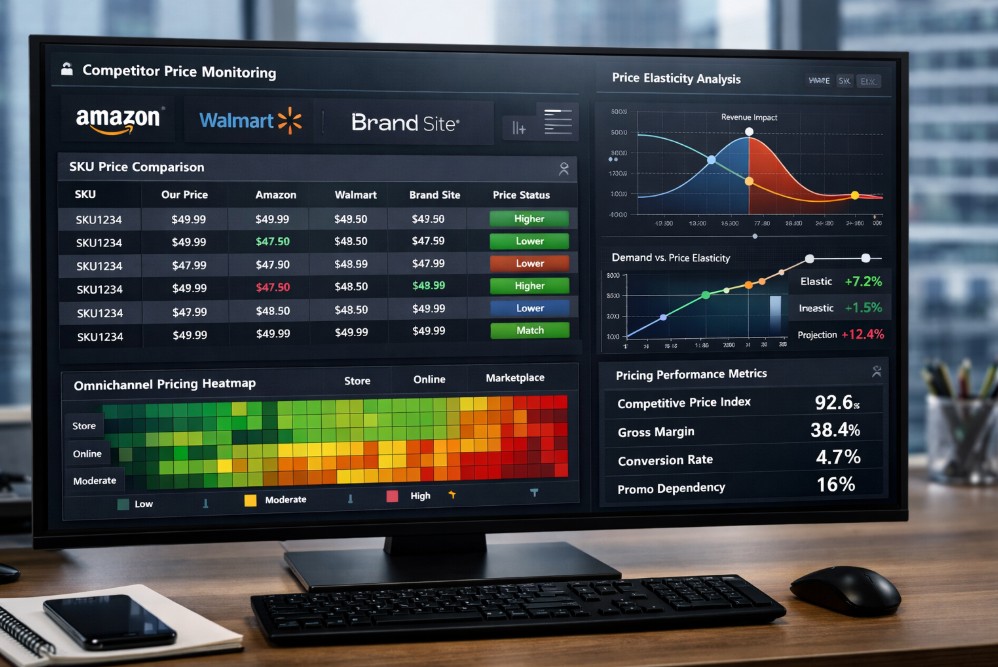
Pricing data accuracy means capturing the correct price for the correct product from the correct seller at the correct time, normalized into a comparable format. Missing any one element introduces decision risk.
Operationally, accuracy has five dimensions.
1. Product matching accuracy
Are you comparing identical SKUs or close substitutes incorrectly merged?
2. Seller attribution
Is the price from a first-party retailer, marketplace seller, or unauthorized reseller?
3. Time relevance
Was the price active when captured or already outdated?
4. Normalization logic
Are shipping, bundles, currency, and promotions handled consistently?
5. Coverage completeness
Are key competitors or channels missing?
Most organizations unknowingly optimize for one dimension while sacrificing others.
tgndata acts as a validation layer by exposing these dimensions instead of hiding them behind a single price field.
Pricing data inaccuracies usually stem from SKU mismatches, retailer variability, promotional complexity, and lack of human validation. Automation scales collection faster than it improves trust.
Common failure points include:
Product title drift across retailers
Regional SKUs treated as identical
Temporary promotions misread as price changes
Bundles and multipacks collapsed into singles
Cause leads to effect, which then scales. One incorrect match feeds alerts, dashboards, and pricing models simultaneously.
As automation expands, error amplification becomes the dominant risk, not data gaps.
Situation: A fashion retailer automated global matching.
What breaks: Size and color variants collapsed into one SKU.
What changes: Tiered matching rules for hero SKUs restored accuracy.
Strategic takeaway: Not all products deserve the same automation logic.
Inaccurate pricing data erodes margin by triggering unnecessary reactions and masking real threats. Teams either chase false competitors or miss genuine price pressure.
Margin loss rarely happens through dramatic errors. It happens through repeated small decisions.
Examples include:
Lowering prices to match a reseller, not a competitor
Holding prices while a key rival quietly discounts
Overreacting to short lived promotions
Signal based diagnostics reveal this pattern. Warning signs include frequent price reversals, high alert volumes with low business impact, and pricing meetings dominated by data debates rather than strategy.
tgndata enables monitoring at scale while flagging anomalies that require human review instead of automated reaction.
Situation: A consumer goods brand saw declining margins despite stable volumes.
What breaks: False undercut alerts triggered unnecessary price drops.
What changes: Accuracy filters reduced alerts by 38 percent.
Strategic takeaway: Fewer alerts often means better pricing.
Auditing pricing data accuracy requires structured validation across matching, freshness, coverage, and consistency. Spot checks alone are insufficient without a repeatable framework.
A practical audit includes five steps.
Compare multiple data sources for the same SKU.
Review high revenue SKUs regularly.
Identify price movements outside historical norms.
Ensure refresh rates match category volatility.
Confirm all critical competitors are represented.
Situation: A home goods brand questioned declining margins.
What breaks: Weekly updates masked daily competitor moves.
What changes: Higher refresh frequency stabilized pricing.
Strategic takeaway: Latency is an accuracy problem.
Even accurate pricing data fails when disconnected from business context. Accuracy does not equal relevance.
Pricing data must be evaluated alongside:
Elasticity
Inventory position
Brand strategy
Channel conflict
Without context, teams optimize locally and damage globally.
For example, matching a competitor price may protect volume but erode brand positioning. Data must inform decisions, not dictate them.
tgndata serves as an operational backbone by integrating pricing signals into decision workflows instead of isolated dashboards.
Situation: A premium brand reacted aggressively to competitor discounts.
What breaks: Brand perception weakened.
What changes: Contextual pricing guardrails restored control.
Strategic takeaway: Accuracy without strategy is still risk.
| Feature or Capability | Business Benefit | KPI Impact | Role Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| SKU matching validation | Fewer false alerts | Margin stability | Pricing manager |
| Retailer coverage mapping | Clear market view | Revenue growth | eCommerce analyst |
| Price normalization | Comparable insights | Decision confidence | Brand strategist |
| Anomaly detection | Faster issue resolution | Operational efficiency | SEO lead |
Automated pricing typically requires accuracy above 97 percent for core SKUs. Lower accuracy increases the risk of cascading errors and margin loss.
SKU matching issues are the most common cause, especially when products vary by region, bundle, or seller.
Refresh rates should align with category volatility. Highly competitive categories may require multiple daily updates.
Yes. Human review remains critical for high impact SKUs and anomaly resolution.
Yes. Accuracy can be measured through confidence scoring, cross validation, and audit frameworks.
Pricing accuracy is a shared responsibility across pricing, analytics, and commerce teams.
Pricing data accuracy is not a technical hygiene task. It is a strategic decision about how much risk your pricing organization is willing to accept.
Teams that measure accuracy, expose confidence, and align data with decision context outperform those chasing volume alone.
tgndata enables organizations to move from blind confidence to validated pricing intelligence, turning pricing data into a strategic asset rather than a liability.





We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!