- Product
- Solution for
For Your Industry
- Plans & Pricing
- Company
- Resources
For Your Industry
Dynamic Pricing Models Explained is essential reading for any organization operating in competitive, fast moving digital markets. Pricing has shifted from a static, spreadsheet driven decision to a continuous system that reacts to demand, competition, and customer behavior.
In modern ecommerce and digital commerce environments, prices are no longer reviewed quarterly or even monthly. They are adjusted daily, hourly, or in near real time. Dynamic pricing models are the systems that make this possible.
This article explains what dynamic pricing models are, how they work, the different types in use today, and how businesses implement them responsibly without damaging trust or margins.
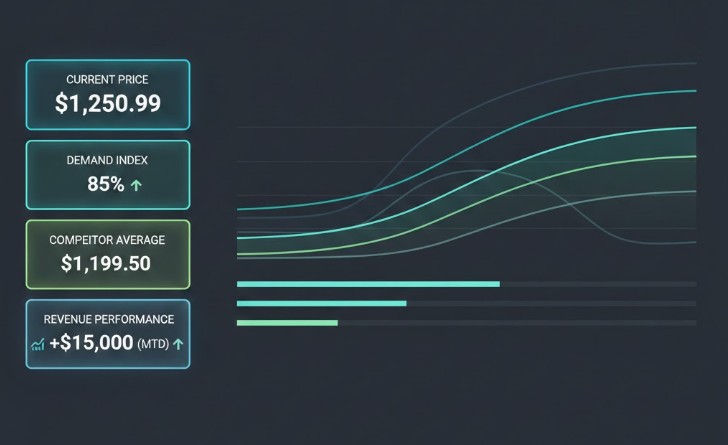
Dynamic pricing models are structured methods for adjusting prices based on data such as demand, competition, inventory levels, or customer behavior. They replace static price lists with systems that continuously respond to market conditions.
Traditional pricing approaches assume stable demand and limited competition. In reality, digital markets change constantly. Static prices quickly become outdated, leading to lost revenue, unnecessary discounting, or competitive disadvantage.
Dynamic pricing models define how prices should change when conditions change. These models can be simple rule sets or advanced algorithms, but they always rely on data inputs, decision logic, and execution mechanisms.
Dynamic pricing does not mean random price changes. It means controlled, explainable adjustments aligned with business objectives.
To function correctly, pricing models need reliable data, clear logic, and monitoring.
tgndata centralizes pricing inputs and ties pricing logic directly to measurable KPIs, ensuring models remain aligned with strategy.
Dynamic pricing models fall into several categories, including rule based, demand based, competitor based, and algorithmic models. Each serves different business needs and maturity levels.
Problem
Many teams need fast, predictable pricing decisions but lack data science resources.
Best Practice Method
Rule-based models adjust prices when predefined conditions are met. Examples include lowering prices when inventory exceeds thresholds or increasing prices during peak demand periods.
Rule-based models are transparent and easy to govern. They are often the starting point for pricing maturity.
How tgndata supports this
tgndata enables teams to deploy rules at scale, monitor outcomes, and adjust logic without engineering bottlenecks.
Problem
Demand fluctuates constantly, yet prices often lag behind real demand signals.
Best Practice Method
Demand-based models adjust prices using signals such as traffic volume, conversion rates, or sales velocity. When demand increases, prices rise within constraints. When demand softens, prices adjust downward.
Problem
Competitors update prices faster than internal teams can respond manually.
Best Practice Method
Competitor-based models adjust prices relative to market benchmarks. These models ensure competitiveness without blindly matching the lowest price.
How tgndata supports this
tgndata automates competitor monitoring and pricing responses while protecting profitability.
Problem
Large catalogs and complex markets overwhelm rule-based approaches.
Best Practice Method
Algorithmic models use historical data to predict optimal prices. Machine learning models continuously improve as more data becomes available.
How tgndata supports this
tgndata provides the data foundation and governance required for advanced pricing models to operate safely.
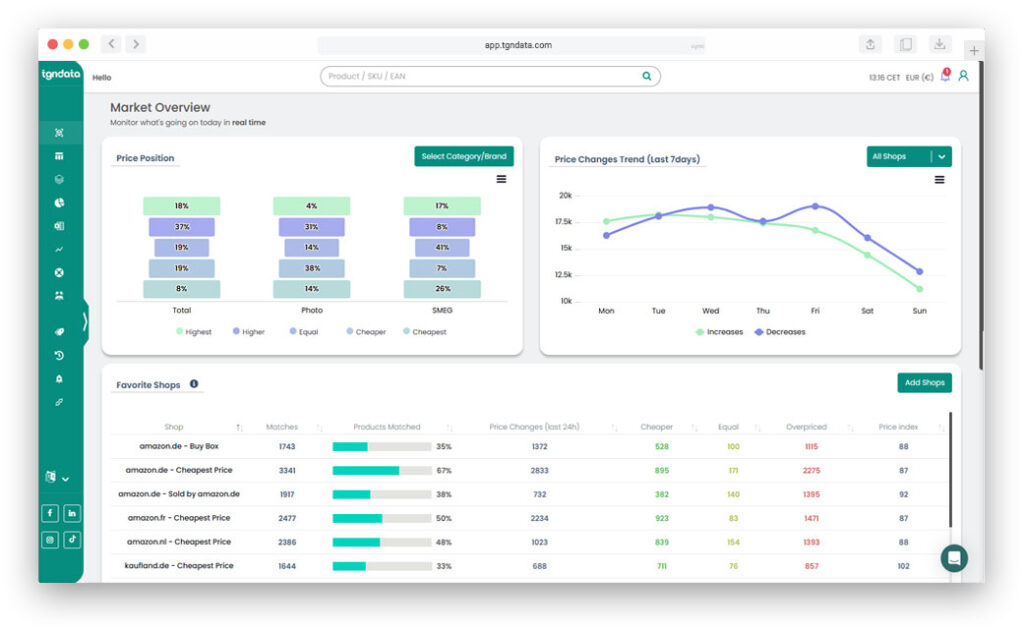
Dynamic pricing models depend on accurate, timely data inputs such as demand signals, competitor prices, costs, inventory, and customer behavior. Poor data quality undermines even the best models.
Organizations often underestimate the complexity of pricing data. Disconnected systems, delayed feeds, and inconsistent definitions lead to incorrect price decisions.
Successful pricing systems establish a unified pricing data layer. This layer validates inputs, checks freshness, and standardizes metrics before pricing logic is applied.
Key data inputs include:
Demand metrics
Cost and margin data
Competitor prices
Inventory availability
Promotional calendars
tgndata aggregates, cleans, and validates pricing data across systems, ensuring pricing models operate on reliable information.
Situation
An e-commerce retailer runs frequent promotions across thousands of SKUs.
What Goes Wrong Without Analytics
Discounts are applied broadly, eroding margin without increasing incremental demand.
Recommended Approach
Use demand elasticity-driven pricing models to tailor discounts based on product sensitivity.
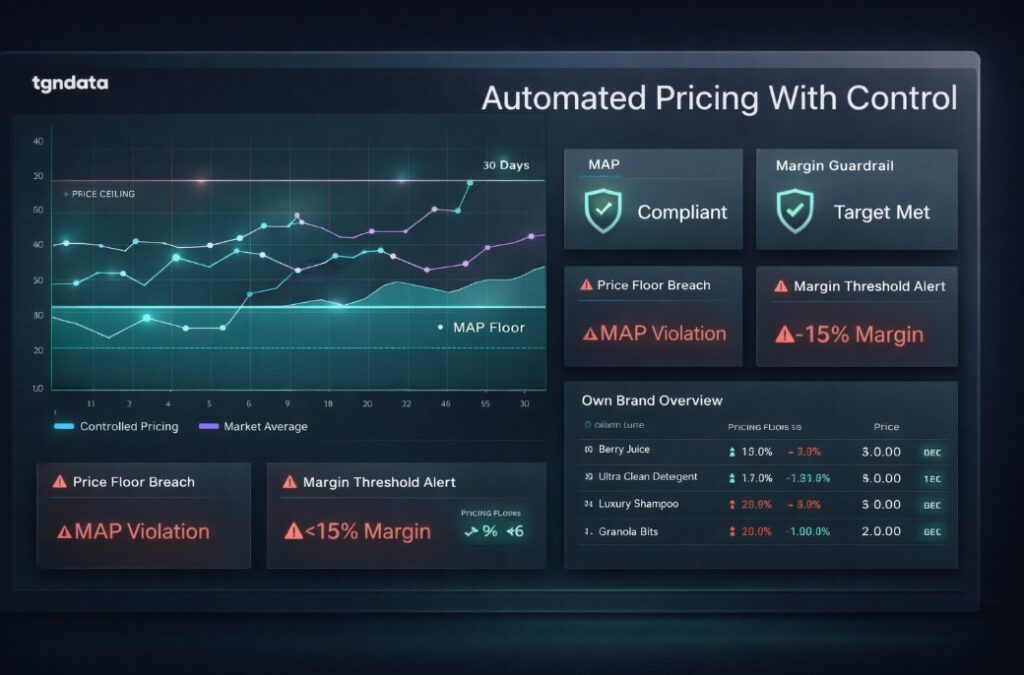
Dynamic pricing introduces risk if not governed carefully. Businesses must define constraints, transparency rules, and monitoring processes to protect margins, trust, and compliance.
Automated pricing without oversight can lead to extreme price swings, customer backlash, or regulatory issues.
Governance frameworks define pricing floors, ceilings, update frequency limits, and approval workflows. Monitoring systems detect anomalies before they cause damage.
Ethical considerations include fairness, transparency, and customer expectations.
tgndata enforces pricing guardrails, maintains audit trails, and provides real time alerts.
Situation
A marketplace updates prices hourly across sellers.
What Goes Wrong Without Governance
Prices fluctuate excessively, confusing customers and reducing trust.
Recommended Approach
Introduce smoothing logic and frequency controls.
What tgndata Enables
Controlled price update cadence and exception alerting.
Implementing dynamic pricing models requires clear objectives, phased rollout, testing, and continuous monitoring. Successful teams start simple and evolve in complexity over time.
Organizations often attempt advanced pricing models without foundational readiness.
Implementation typically follows these stages:
Define pricing objectives
Audit data readiness
Select initial model type
Test on limited scope
Monitor performance
Scale responsibly
tgndata supports phased pricing maturity, enabling gradual expansion without operational risk.
| Feature or Capability | Business Benefit | KPI Impact | Primary Role Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated pricing rules | Faster market response and reduced manual effort | Revenue uplift | Pricing Manager |
| Competitor price monitoring | Maintains competitive positioning without margin erosion | Conversion rate | eCommerce Analyst |
| Elasticity insights | Enables targeted discounts instead of blanket promotions | Gross margin | SEO Lead |
| Pricing governance controls | Protects brand trust and prevents pricing volatility | Price stability | Brand Strategist |
Situation
A direct to consumer brand expands into new regions.
What Goes Wrong Without Automation
Pricing becomes inconsistent across markets, confusing customers.
Recommended Approach
Regional dynamic pricing models with centralized oversight.
What tgndata Enables
Localized pricing logic with global governance.
A strong pricing intelligence platform should integrate data, support explainable logic, enforce governance, and measure performance against KPIs.
Key evaluation criteria include:
Data coverage
Transparency
Scalability
Role based controls
Common pitfalls include black box algorithms, weak governance, poor data integration, and misalignment with business objectives.
tgndata emphasizes explainability, control, and alignment with commercial goals.
The main goal is to adjust prices using data to improve revenue, margin, or conversion while responding to changing market conditions in a controlled way.
No. Smaller businesses can use rule based dynamic pricing models effectively before adopting advanced approaches.
Price change frequency depends on industry norms and customer expectations. Governance rules should limit excessive volatility.
No. Many successful models rely on rules or basic analytics. Machine learning becomes valuable at scale.
Demand signals, competitor prices, and cost data are the most critical inputs.
Yes, if poorly governed. Transparent rules and stable behavior reduce this risk.
Dynamic pricing models are not about chasing every market movement. They are about building disciplined systems that translate data into controlled, measurable pricing decisions.
When pricing is treated as an operational system rather than a one time decision, businesses gain resilience, agility, and sustainable growth.
tgndata helps organizations move from pricing theory to production ready pricing systems that scale with confidence.




We use cookies to provide you with an optimal experience, for marketing and statistical purposes only with your consent, which you may revoke at any time. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.






Missing an important marketplace?
Send us your request to add it!